Fermenter Technologies, a leading name in bioprocess equipment manufacturing, aims to simplify this understanding by explaining the difference between fermenter and bioreactor in clear and practical terms. Our company continues to offer world-class equipment solutions that enhance productivity and innovation in the biotech industry. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone involved in microbial processes, pharmaceutical production, or biochemical engineering.
Difference Between Bioreactor and Fermenter
A fermenter is a closed vessel used primarily for the growth of microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast, or fungi under controlled conditions to produce biochemical products like alcohol, enzymes, antibiotics, or organic acids. In contrast, a bioreactor is a broader term used to describe any device or system that supports a biologically active environment not limited to microorganisms but also including plant, animal, and insect cells for various biotechnological applications.
Fermenters are mainly used for microbial fermentation, whereas bioreactors are used for a wide range of biological processes including tissue culture, cell cultivation, and enzyme production.
Fermenter Technologies designs both fermenters and bioreactors that are tailored to meet specific industry needs. We provide customized solutions that ensure efficient growth, product yield, and process control for research as well as industrial-scale production.
Applications in Industry
Fermenters
Fermenters are extensively used in:
- Food and Beverage Industry (beer, wine, yogurt, and vinegar production)
- Pharmaceutical Industry (production of antibiotics, enzymes, and vitamins)
- Biofuel Industry (ethanol and biogas production)
- Chemical Industry (organic acid synthesis)
Bioreactors
Bioreactors find application in:
- Biopharmaceutical Production (vaccines, antibodies, therapeutic proteins)
- Tissue Engineering (culturing cells for regenerative medicine)
- Environmental Engineering (wastewater treatment and bio-remediation)
- Agriculture (biofertilizer and biopesticide production)
With this diversity, it is evident that while fermenters serve mainly microbial industries, bioreactors serve a wider spectrum of biological processes.
What is a fermenter ? How does it work
A fermenter is a vessel specifically designed to carry out fermentation. Fermentation is a biological process where microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, or yeast break down organic compounds, often sugars into simpler products like alcohol, acids, or gases. The design of a fermenter focuses on maintaining an environment conducive to microbial growth, ensuring factors like temperature, pH, oxygen supply, and sterility are carefully controlled.
What is a bioreactor ?
A bioreactor is a more versatile system designed to support a variety of biological processes, not limited to fermentation. It provides a controlled environment for growing animal cells, plant cells, stem cells, and even tissues, in addition to microorganisms. While fermenters focus largely on microbial processes, bioreactors extend their scope to more complex systems involving sensitive cell cultures.
Also Read: Scale Up of Fermentation Process
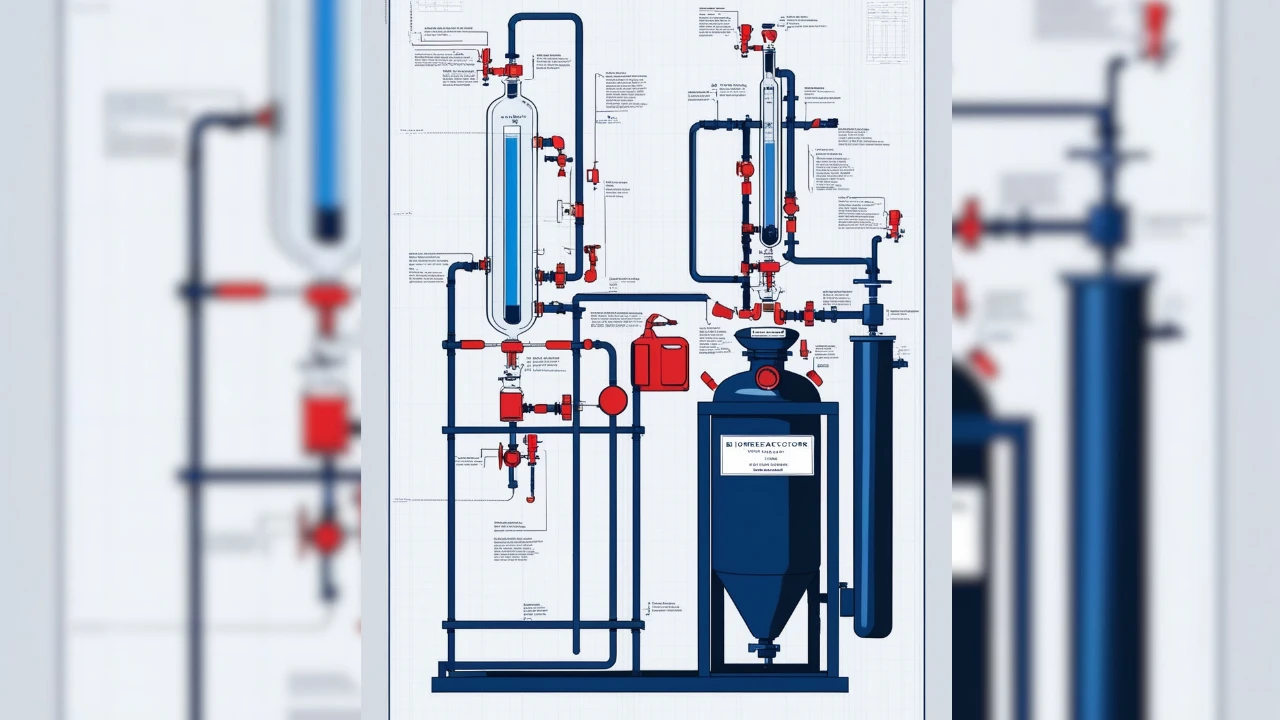
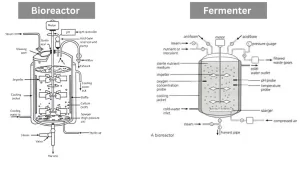
Fermenter and Bioreactor diagram
Key Difference Between Fermenter and Bioreactor
| Aspect | Fermenter | Bioreactor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A vessel used for microbial fermentation under controlled conditions. | A device used for any biological reaction involving living cells or enzymes. |
| Application | Used mainly for microbial processes like alcohol, antibiotic, or enzyme production. | Used in broader biological processes including cell culture, tissue engineering, and vaccine production. |
| Organisms Used | Microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and yeast. | Microorganisms, plant cells, animal cells, and insect cells. |
| Process Type | Primarily used for fermentation processes (aerobic or anaerobic). | Used for various bioprocesses beyond fermentation. |
| Control Parameters | Focuses mainly on temperature, pH, aeration, and agitation. | Controls more complex factors like gas composition, shear stress, nutrient feed, and cell density. |
| Example | Beer brewing or antibiotic production. | Production of monoclonal antibodies or recombinant proteins. |
Why Choose Fermenter Technologies
Fermenter Technologies is a leading manufacturer of high-performance fermenters and bioreactors. Our commitment to quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction makes them a preferred partner for research institutions and industries alike. We offer complete solutions — from conceptual design and installation to maintenance and after-sales support.
Some reasons to choose Fermenter Technologies include:
- Use of high-grade materials for durability and hygiene.
- Custom-built designs based on process requirements.
- Advanced control and automation systems.
- Comprehensive support and training for operators.
- Proven expertise in both microbial and cell culture technologies.
Fermenter Technologies continues to lead the way by designing advanced equipment that meets the evolving needs of the bio-industry. We offer customized, efficient, and reliable fermenters and bioreactors, they empower industries to achieve higher productivity and consistent results. Whether you are looking for a specialized fermenter or a versatile bioreactor, Fermenter Technologies is your trusted partner in innovation and excellence.